Minecraft on Kubernetes
In this example, we'll demonstrate the Kubernetes Connector with a simple workload - a Minecraft server!
You can use any Kubernetes cluster, as long as your kubeconfig is set up correctly. Here, we'll use a k3s cluster running on our local machine. Check the k3s {Quick-Start Guide](https://docs.k3s.io/quick-start) to set up a cluster of your own.
For this example, we have a repo with a script and config ready to go. It's designed to run against your default kubeconfig.
We'll start with our autoschematic.ron file. Remember, this should be at the root directory of a Git repo.
If you haven't installed the k8s connector already, run autoschematic install to build and install it.
Importing Existing Resources
We'll start by running bash scripts/minecraft-k3s.sh up to install and start the Minecraft server on our cluster. You can skip this if you'd prefer to just poke around your Kubernetes cluster in its current state.
You can connect to the server on localhost:30065 .
Now, we'll scan our cluster and import its resources into code by running autoschematic import.
Fantastic! See what we did there, by the way? We used the subpath filter syntax to limit the set of resources we import.
Since addresses have strong semantic significance in Autoschematic, this is a very useful operation. Plan, apply, import, and other commands all support filtering by subpath with --subpath or -s. See the command-line help page for more.
First, we'll commit our state to git, assuming everything went well.
Now, let's take a look at our configmap.
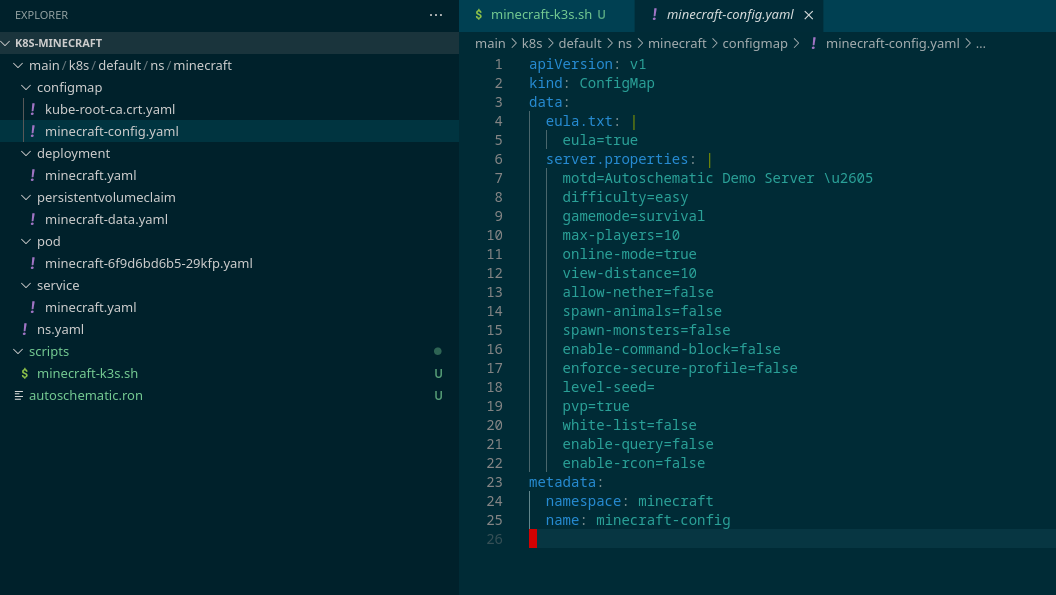
Oh! No mobs and no nether? We'll just fix that. We'll modify our config and stage it with git add, but we won't commit it yet.
To restart the pod, we'll also delete the pod file and git add that, too!
Cool! Now, the deployment should spawn a new pod with your updated configuration. You can connect to the Minecraft server on the address localhost:30065.
Oh, and one extra note - if you're using the Visual Studio Code extension, you can instantly get the diff between your Autoschematic resources and their live state like so: